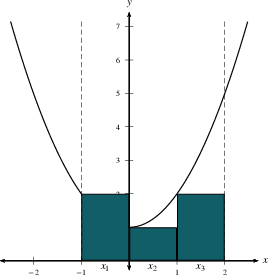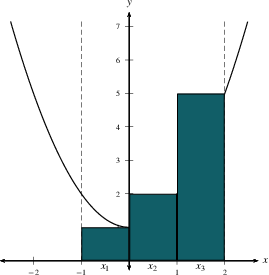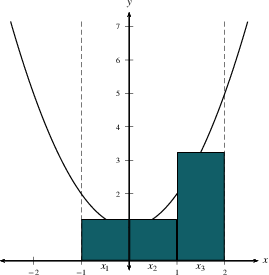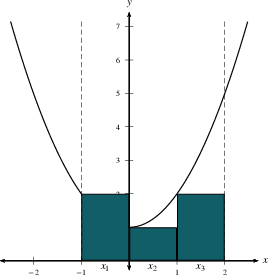
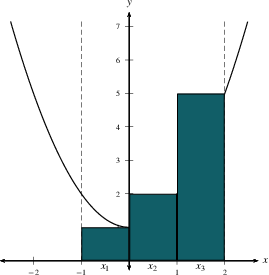
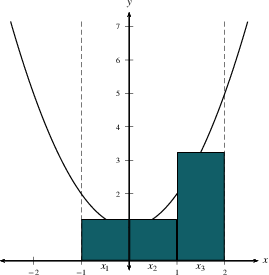
The total area under $y=f(x)$ on an interval is approximated by $$\sum_{i=1}^n \,f(x_i^*)\, \Delta x,$$ which is the sum of the areas of $n$ rectangles.
This sort of expression is called a Riemann Sum
We use the Greek letter sigma ($\Sigma$) to mean "sum". The expression
"$\displaystyle{\sum_{i=1}^n (\hbox{formula involving $i$})}$" means
The notation for Riemann Sums can be complicated. Keep referring to the left side for a list of symbols.
Notation:
|
The exact area is the limit of the Riemann sum as $n \to \infty$.
Notice that we could use the left endpoint
$x_{i-1}$, the right endpoint $x_i$, the midpoint
$\frac{x_{i-1}+x_i}{2}$, or any other representative point.