- The function may have a discontinuity, e.g.,
the function below at $x=-1$

- The function may have a sharp change in direction,
e.g., $f(x) = |x|$ at $x=0$.

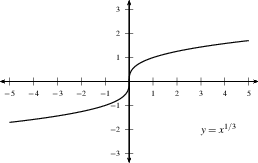
- The function may have a vertical tangent,
e.g., $f(x) = x^{1/3}$ at $x=0$.