Example 2: Reverse the order of integration
in the iterated integral
$$I \ = \ \int _0^2\left(\int_{x^2}^4\, f(x,\,y)\, dy\right)dx\,,$$
but make no attempt to evaluate either integral.
Solution: The region of integration is the set
$$D \ = \ \Bigl\{\,(x,\,y) : \, x^2 \le y \le 4\,, \ \ 0 \le x \le
2\,\Bigr\}$$ whose graph is shown below. The given repeated
integral fixes $x$ and integrates with respect to $y$ along the
vertical black line. To reverse the order of integration we need to
fix $y$ and integrate with respect to $x$ along the red line. To set
up the repeated integral we have to express $D$ in the form $$D \ = \
\Bigl\{\,(x,\,y) : \, \phi(y) \le x \le \psi(y)\,, \ \ c \le y \le
d\,\Bigr\}$$ for suitably chosen $c,\, d$ and functions $\phi(y),\,
\psi(y)$.
Now by inverse functions, the parabola $y = x^2$ can
be written as $x = \sqrt{y}$; this tells us how to find the right hand
limit of integration $x = \psi(y)$.
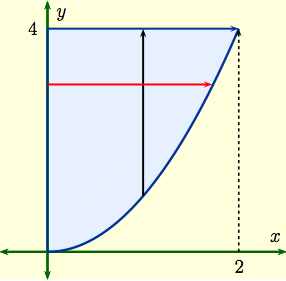
On the other hand, the graph above shows the left hand
limit is $x = 0$. Thus $D$ can also be written as
$$D \ = \ \Bigl\{\,(x,\,y) : \, 0 \le x \le \sqrt{y}\,, \ \ 0 \le y \le 4\,\Bigr\}\,.$$
Consequently, reversing the order of integration shows that
$$I \ = \ \int _0^4\left(\int_0^{\sqrt{y}}\,
f(x,\,y)\, dx\right)\,dy\,,$$
integrating now first with respect to $x$. |