For example, the series $$ \sum_{i=0}^\infty\left(\frac{1}{3}\right)^i=1+\frac13+\frac19+\frac{1}{27}+\ldots $$ is geometric with ratio $r=\frac13$.
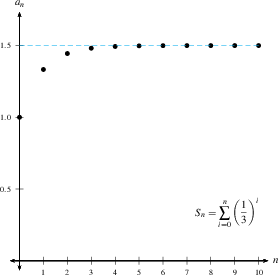
A geometric series is a
series where the ratio between successive terms is constant.
You can view a geometric series as a series with terms that form a
geometric sequence (see the previous module on sequences).
For example, the series $$ \sum_{i=0}^\infty\left(\frac{1}{3}\right)^i=1+\frac13+\frac19+\frac{1}{27}+\ldots $$ is geometric with ratio $r=\frac13$. |
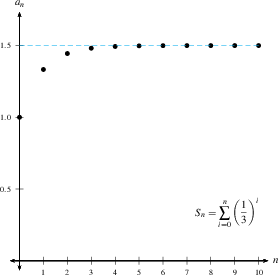 |
Geometric series are our favorite series. It is always possible, and even easy, to
determine whether a geometric series converges, and if it
does, its value. This is rarely possible with
other types of series.
| The geometric
series $\displaystyle\sum_{i=0}^\infty a
r^i=a+ar+ar^2+ar^3 + \ldots$ converges to
$\displaystyle\frac{a}{1-r}$ if $-1<r<1$ and
diverges otherwise. Warning: this
value of the series is true only when the series begins
with $i=0$, so that the first term is $a$. |
The main issue is to confirm that a series is
indeed geometric, and if so, what the values of $a$ and $r$ are.
Example: $5-\tfrac {10}{3}+\tfrac{20}
{9}-\tfrac{40}{27}+\tfrac{80}{81}+\cdots.$
Solution: First, we try to determine if it is a
geometric series. Dividing each term by the previous term
shows that we have a common ratio of $r=-\tfrac 2 3$, with
$a=a\cdot r^0=5$. So we have a geometric series, and since
$|r|<1$, the series converges. Its value is
$\frac{a}{1-r}=\frac{5}{1+\tfrac 2 3}=\frac{5}{\tfrac 5
3}=3$.
We have determined that $\displaystyle\sum_{n=0}^\infty
5\left(-\frac{2}{3}\right)^n=3$.
------------------------------------------------------------
Example: $3-\tfrac 6 5 +
\tfrac{12}{25}-\tfrac{24}{125}+\cdots$.
DO: Find $r$
and $a$, and evaluate this series.
Solution:
$\displaystyle\sum_{n=0}^\infty3\cdot\left(-\frac{2}{5}\right)^n=\frac{15}{7}$.