[THIS PROBLEM IS ESSENTIALLY EXAMPLE 6 ON PAGES 205-7, ONLY SHIFTED OVER BY ONE]
Consider the function ![]()
a) Find the partition points of f (if there are any) and make a sign chart for f.
Since ![]() is always positive, the only partition point is at x-1=0, that is
at x=1. f(x) is positive for x > 1 and negative
for x < 1.
is always positive, the only partition point is at x-1=0, that is
at x=1. f(x) is positive for x > 1 and negative
for x < 1.
b) Find the critical points of f (if there are any) and make a sign chart for f'.
![]() . The only critical point is at x=0.
f'(x) is positive
for x > 0 and negative for x < 0. Put another way,
f(x)
is decreasing for x < 0 and increasing for x > 0, so there
is a (local and also absolute) minimum at x=0.
. The only critical point is at x=0.
f'(x) is positive
for x > 0 and negative for x < 0. Put another way,
f(x)
is decreasing for x < 0 and increasing for x > 0, so there
is a (local and also absolute) minimum at x=0.
c) Find the inflection points of f (if there are any) and make a sign chart for f''.
![]() and there is an inflection point at x=-1. f''(x) is
positive for x > -1 and negative for
and there is an inflection point at x=-1. f''(x) is
positive for x > -1 and negative for
x < -1, so the curve is concave down for x < -1
and concave up for x > -1.
d) Sketch the graph of the function. Show clearly the location of the partition points, critical points and inflection points.
Sorry, but I don't know how to draw a graph on screen. Imagine the graph on page 207, shifted to the right by one unit.
Problem 2. Max-min
Find the absolute maximum and absolute minimum values of the function ![]() on the interval [-1,4].
on the interval [-1,4].
The extrema must occur at the critical points or at the endpoints. So
first we find the critical points: ![]() , so x=0 or x=2. The endpoints are of course x=-1
and x=4. So our four candidate points are x=-1, 0, 2 and
4. We then evaluate:
, so x=0 or x=2. The endpoints are of course x=-1
and x=4. So our four candidate points are x=-1, 0, 2 and
4. We then evaluate:
f(-1) = -2, f(0)=2, f(2)=-2, f(4)=18.
The maximum value is f(x)=18 and is achieved at x=4. The minimum value is f(x)=-2 and is achieved at two points, x=-1 and x=2.
Problem 3. More optimization
A gardener wants to build a rectangular fence to enclose as big a garden as possible. One side of the fence needs to be heavy-duty to keep out the local deer. This side costs $3/foot. The other three sides can be made of cheaper materials and cost only $1/foot. The gardener has budgeted $80 for the project. You need to design the optimal layout for him by following these steps:
a) Define your variable (call it x) and compute the area A(x) as a function of x. What are the possible values of x?
Let x be the length of the expensive side (and also the length
of the side opposite it). Let y be the length of the other two sides.
The total cost is 3x + x + y + y = 4x+2y.
Since our budget is $80, we must have 4x+2y=80, or y=40-2x.
The area is ![]() .
x must be at least 0, and at most 20 (since if x=20 then
y=0).
.
x must be at least 0, and at most 20 (since if x=20 then
y=0).
To summarize, we are maximizing the function ![]() on the interval [0,20].
on the interval [0,20].
b) Maximize the function A(x).
Find the critical point(s): 0=A'(x)=40-4x, so x=10. Since A''(10)=-4 < 0, this is a local max. Since it's the only critical point, it is a global max. The area is then A(10)=200.
c) Interpret your results: How much area can the gardener fence in? What is the shape of the optimal garden?
The gardener can fence in 200 square feet by building a 10 by 20 foot rectangle, with the expensive stretch being along the 10 foot side.
Problem 4. Implicit differentiation
Consider the curve
![]()
a) Find dy/dx at the point (x,y).
Take the derivative of the equation and solve for y':
![]() , so
, so 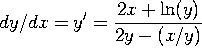 .
.
b) Find the slope of the line tangent to the curve at (1,1).
Evaluating this at x=y=1 we get dy/dx = (2+0)/(2 - 1/1)=2/1=2.
c) Estimate the value of y when x=1.05.
x=1 and dx=0.05. ![]() .
.
Problem 5. Exponential Growth
A colony of hamsters contains 1000 hamsters and is growing at a rate of 3.5%/day, compounded continuously. (Of course, this is only an approximation, since in reality the number of hamsters at any moment is an integer. But for purposes of this problem we will pretend that the population is a continuous quantity, growing continuously).
a) How many hamsters will there be in 30 days? Write down an
exact
answer. (That is, something like ![]() , not something like 2,857.651)
, not something like 2,857.651)
![]() (which is approximately 2,857.651, by the way).
(which is approximately 2,857.651, by the way).
b) When will the population hit 4000? Again, give an exact answer.
Solve ![]() , so
, so ![]() , so
, so ![]() , so
, so ![]() .
.
c) Using the fact that ![]() , estimate your answer to part (b). Your answer should be numerical, e.g.
``In 50 days''. The correct answer is fairly simple and yes, you can get
it without a calculator.
, estimate your answer to part (b). Your answer should be numerical, e.g.
``In 50 days''. The correct answer is fairly simple and yes, you can get
it without a calculator.
![]() , so
, so ![]() days.
days.
Problem 6. Taking derivatives
Take the derivatives, with respect to x, of the following functions.
Your final answer should be expressed entirely in terms of x. (e.g. ![]() , not
, not ![]() ). However, you do NOT need to simplify your results further.
). However, you do NOT need to simplify your results further.
a)![]()
Use the product rule: ![]() .
.
b) ![]()
Use the chain rule: 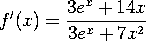
c) ![]()
Use the chain rule: ![]() .
.
d) ![]()
If you use the chain rule, applied twice, you get
![]()
But you could also realize that the log of e to the something is that
something, so ![]() and f'(x)=2x.
and f'(x)=2x.