Main page
Chapter 10: Parametric Equations and Polar Coordinates
Chapter 12: Vectors and the Geometry of Space
Learning module LM 12.1: 3-dimensional rectangular coordinates:
Learning module LM 12.2: Vectors:
Vectors in 2 dimensionsVectors in 2 dimensions p2
Components and combinations
On to 3 dimensions
Learning module LM 12.3: Dot products:
Learning module LM 12.4: Cross products:
Learning module LM 12.5: Equations of Lines and Planes:
Learning module LM 12.6: Surfaces:
Chapter 13: Vector Functions
Chapter 14: Partial Derivatives
Chapter 15: Multiple Integrals
Vectors in 2 dimensions
If ${\bf u}$ and ${\bf v}$ are vectors and $a$ and $b$ are numbers, then any vector of the form $a\,{\bf u} + b \,{\bf v}$ is called a linear combination of ${\bf u}$ and ${\bf v}$. Most problems with vectors involve figuring out which vectors are linear combinations of which other vectors, and how.
Here's a worked example to illustrate subtraction and scalar multiplication
|
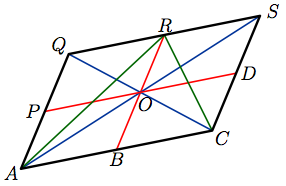
Example 1: when displacement vectors
$${\bf u} \ = \ \overrightarrow{AB}\,, \qquad {\bf v} \ = \ \overrightarrow{AP}\,,$$
are specified by the parallelogram
express $\overrightarrow{CR}$ in terms of $\bf u$ and $\bf v$. |
Solution: By the Parallelogram Law $$\overrightarrow{CR} \ = \ \overrightarrow{CB} +\overrightarrow{CS}\,.$$ But $$\overrightarrow{CB}\ = \ - \overrightarrow{BC}\ = \ - \overrightarrow{AB}\ = \ - {\bf u}\,,$$ while $$\overrightarrow{CS}\ = \ \overrightarrow{AQ}\ = \ 2\,\overrightarrow{AP}\ = \ 2{\bf v}\,.$$ So then $$\overrightarrow{CR} \ = \ 2{\bf v} - {\bf u}\,.$$ |
The following interactive provides a set of examples for you to work on (some involve a bit of geometry and trig!).