
Home
The Six Pillars of Calculus
The Pillars: A Road MapA picture is worth 1000 words
Trigonometry Review
The basic trig functionsBasic trig identities
The unit circle
Addition of angles, double and half angle formulas
The law of sines and the law of cosines
Graphs of Trig Functions
Exponential Functions
Exponentials with positive integer exponentsFractional and negative powers
The function $f(x)=a^x$ and its graph
Exponential growth and decay
Logarithms and Inverse functions
Inverse FunctionsHow to find a formula for an inverse function
Logarithms as Inverse Exponentials
Inverse Trig Functions
Intro to Limits
OverviewDefinition
One-sided Limits
When limits don't exist
Infinite Limits
Summary
Limit Laws and Computations
Limit LawsIntuitive idea of why these laws work
Two limit theorems
How to algebraically manipulate a 0/0?
Indeterminate forms involving fractions
Limits with Absolute Values
Limits involving indeterminate forms with square roots
Limits of Piece-wise Functions
The Squeeze Theorem
Continuity and the Intermediate Value Theorem
Definition of continuityContinuity and piece-wise functions
Continuity properties
Types of discontinuities
The Intermediate Value Theorem
Summary of using continuity to evaluate limits
Limits at Infinity
Limits at infinity and horizontal asymptotesLimits at infinity of rational functions
Which functions grow the fastest?
Vertical asymptotes (Redux)
Summary and selected graphs
Rates of Change
Average velocityInstantaneous velocity
Computing an instantaneous rate of change of any function
The equation of a tangent line
The Derivative of a Function at a Point
The Derivative Function
The derivative functionSketching the graph of $f'$
Differentiability
Notation and higher-order derivatives
Basic Differentiation Rules
The Power Rule and other basic rulesThe derivative of $e^x$
Product and Quotient Rules
The Product RuleThe Quotient Rule
Derivatives of Trig Functions
Necessary LimitsDerivatives of Sine and Cosine
Derivatives of Tangent, Cotangent, Secant, and Cosecant
Summary
The Chain Rule
Two Forms of the Chain RuleVersion 1
Version 2
Why does it work?
A hybrid chain rule
Implicit Differentiation
IntroductionExamples
Derivatives of Inverse Trigs via Implicit Differentiation
A Summary
Derivatives of Logs
Formulas and ExamplesLogarithmic Differentiation
Derivatives in Science
In PhysicsIn Economics
In Biology
Related Rates
OverviewHow to tackle the problems
Example (ladder)
Example (shadow)
Linear Approximation and Differentials
OverviewExamples
An example with negative $dx$
Differentiation Review
How to take derivativesBasic Building Blocks
Advanced Building Blocks
Product and Quotient Rules
The Chain Rule
Combining Rules
Implicit Differentiation
Logarithmic Differentiation
Conclusions and Tidbits
Absolute and Local Extrema
DefinitionsThe Extreme Value Theorem
Critical Numbers
Steps to Find Absolute Extrema
The Mean Value and other Theorems
Rolle's TheoremsThe Mean Value Theorem
Finding $c$
$f$ vs. $f'$
Increasing/Decreasing Test and Critical NumbersProcess for finding intervals of increase/decrease
The First Derivative Test
Concavity
Concavity, Points of Inflection, and the Second Derivative Test
The Second Derivative Test
Visual Wrap-up
Indeterminate Forms and L'Hospital's Rule
What does $\frac{0}{0}$ equal?Examples
Indeterminate Differences
Indeterminate Powers
Three Versions of L'Hospital's Rule
Proofs
Optimization
StrategiesAnother Example
Newton's Method
The Idea of Newton's MethodAn Example
Solving Transcendental Equations
When NM doesn't work
Anti-derivatives
AntiderivativesCommon antiderivatives
Initial value problems
Antiderivatives are not Integrals
The Area under a curve
The Area Problem and ExamplesRiemann Sum Notation
Summary
Definite Integrals
Definition of the IntegralProperties of Definite Integrals
What is integration good for?
More Applications of Integrals
The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus
Three Different ConceptsThe Fundamental Theorem of Calculus (Part 2)
The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus (Part 1)
More FTC 1
The First Derivative Test
Remember that critical numbers are the only places where a function can have a local maximum or minimum, and are the only places where $f'(x)$ can change sign. These ideas are related by
The First Derivative Test: Let
$c$ be a critical number for a continuous function $f$
|
Notice: A critical number may indicate a local extrema, but some critical numbers do not yield local extreme values. This is the circumstance indicated in number 3. above.
In the examples below, we have included both $f$ and $f'$ in each of the 8 graphs. You can see the relationship between the sign of $f'(x)$ (the slope of the tangent line at $x$, positive or negative) and the direction of $f$ at $x$ (increasing or decreasing). DO: Study these examples. Find those where the critical number does not yield a max or min.
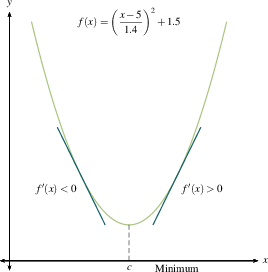
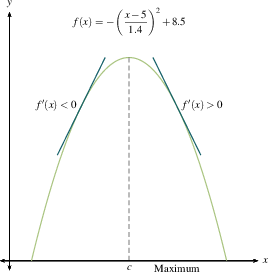
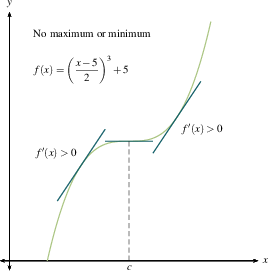
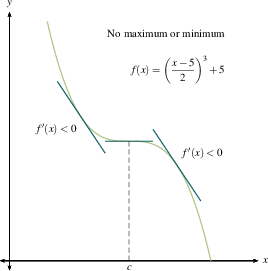
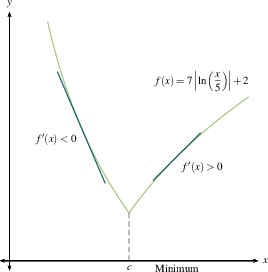
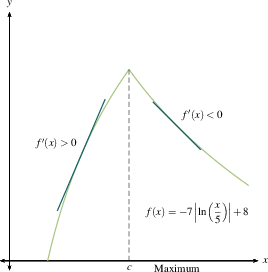
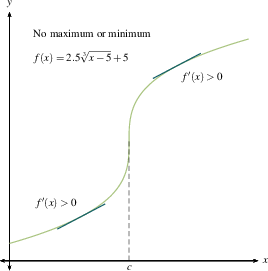
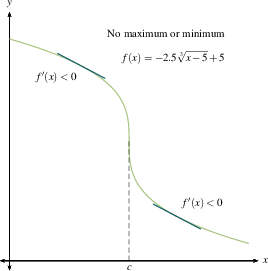
The first derivative test makes sense. A local maximum is where you stop going up and start coming down. A local minimum is where you stop going down and start coming up. If you flatten out and then resume going in the direction you were already heading, you're at a critical point but not at a maximum or minimum. Once you make a number line with intervals between critical numbers for $f'(x)$, as we outlined previously, then you will know where all the local extreme values are.
Example: Find the local maxima and minima of $f(x)=x^3-3x^2$.
Solution: In a previous slide, we determined that $f'(x)$ is positive on $(-\infty,0)$, negative on $(0,2)$ and positive on $(2,\infty)$. Since $f'$ goes from positive to negative at $x=0$, there is a local maximum at $x=0$. Since $f'$ goes from negative to positive at $x=2$, there is a local minimum at $x=2$.